This year, Fundación CANNA has carried out a study on the microbiological quality of the Cannabis offered in Cataluña's Cannabis social clubs (CSC). The results will be shown at the end of the year.
Cannabis, like any other plant or food, can contain microbiological contaminants potentially harmful for our health. These contaminants are some types of bacteria and fungi that could end up appearing or developing in the final product. It will depend on the growing, drying, processing, preservation and handling of the plant.
Samples from several clubs from Cataluña were analysed in the laboratory. A total of 55 samples from 31 CSC.
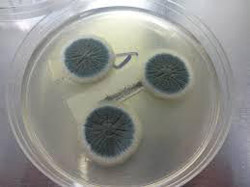
Fungal growth in plate
In order to determine the microbiological level of the samples analysed, two factors have been taken into account: the total number of microorganisms present in each sample, and the absence of microorganisms with high pathogenic potential. A high number of microorganisms, irrespective of the kind of microorganism, indicates that the production, preservation and/or handling processes haven't been properly managed. Nowadays, some US states are establishing microbiological limits for the Cannabis provided in their dispensaries.
The data obtained shows the total amount of fungi and enterobacteria found in the samples of Cannabis. Additionally, the different fungi were identified and the presence of pathogenic bacteria such as Salmonella and E. coli. was sought.
The amount of microorganisms is measured in colony-forming units (CFU) per gramme of product analysed. It tells us the number of spores, or parts of the microorganism, that could grow and develop, becoming a mass called a colony.
The microbiological analysis was conducted in collaboration with Pharmacology Professor, Manuel Pérez (Madrid). Manuel first studied the microbiological contamination in hash samples.
The samples were also analysed to determine the content of cannabinoids. The volume of information about the effect produced by the combination of cannabinoids CBD and THC is constantly increasing. Because of this, it is crucial that consumers know the amount of each cannabinoid present in the product, in order to choose the varieties that better suit their needs. With this information, consumers can also predict the effect derived from a particular variety. A better targeted use and a more accurate dosage will be possible.
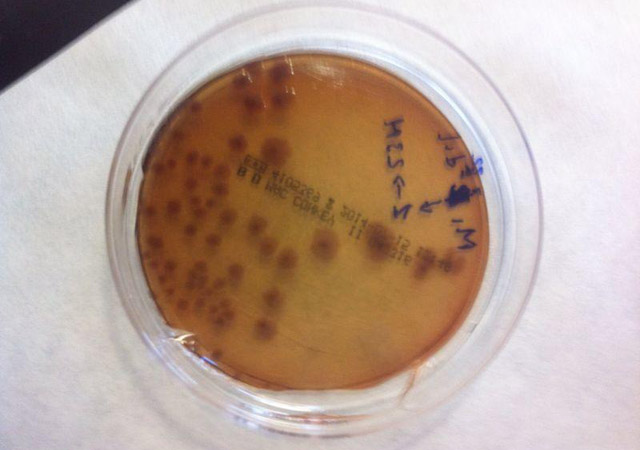
Bacterial growth in plate
Fungi and yeasts
The total number of CFU per gramme present in the samples was counted in the analysis. Some fungi were identified while looking specifically for Aspergillus and other potentially harmful fungi.
The genus Aspergillus encompass several fungi species, many of which can cause serious damage to health. Some of them produce micotoxins called aflatoxins, which are substances with a high toxic potential for the body.
Aspergillus can cause aspergillosis, which is a disease where this fungus can develop within the body. When this happens, a mass of cells forms around the fungus to isolate it from the rest of the body. This mass is called aspergilloma. When speaking about healthy individuals, the body can generally fight against these pathogens and eliminate them. However, in those cases in which there is a special sensitivity to the fungus, or in which the individual is immunodeficient, Aspergillus can win the battle. Some of these cases take place in individuals suffering from HIV, those who have undergone a transplant and in people who are being treated against cancer with chemotherapy or radiotherapy, or sufferers of asthma.
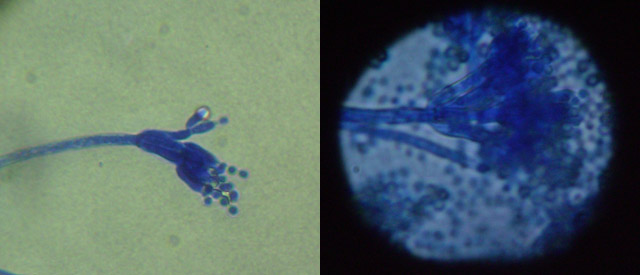
The fungi's structures will be examined under a microscope for their identification.
These fungi generally develop in products with a high rate of humidity, so a slow drying process, or inadequate preservation, are the factors that can influence their development the most. Furthermore, it has been shown that spores can reach the lungs when inhaled by smoking cigarettes. Several cases of aspergillosis caused by inhalation of Cannabis polluted with this fungus have been reported.
Other fungi which can appear in Cannabis are those of the genus Mucor. Some of these fungi can cause the so-called murcomycosis. As with Aspergillus, the fungus develops in different organs, specially in the brain, lungs and skin, causing severe pathologies.
Genus Penicillium can be present too. Some species are used to make cheese or penicillin. However, others can produce micotoxins. People allergic to penicillin should avoid contact with these fungi.
Cladosporium is another genus of fungi that can be found in Cannabis. Even though it is not common, it can cause severe pathologies that can be a problem in certain cases, especially for people with respiratory deficiencies.
Enterobacteria and bacteria resistant to bile

Enterobacteria are a wide group of bacteria, which can colonise the digestive tract. Many of them can be found in stools, although they can also inhabit the soil.
Some of them don't pose a risk to human health. Nevertheless, others such as Salmonella and E. Coli can cause serious damage.
The way in which these bacteria cause an infection in the body, is through their ingestion. The most common means of transmission is during the making of cigarettes.
Due to the contact of the fingers with the polluted material, part of these organisms remain adhered to the skin. When we handle food or put fingers in the mouth, these bacteria can get into the body and cause infection.


